The iterative model is a software
development life cycle (SDLC) approach in
which the initial development is started based on the initial requirements that are clearly defined and subsequent features are added to the base software product through iterations
until the final system is completed. At each
iteration, design modifications are made and new functional capabilities are
added. The basic idea behind this method is to develop a system through
repeated cycles (iterative) and in smaller portions at a time (incremental).
Unlike the more traditional waterfall model, which focuses on a step-by-step process of development stages, the iterative model is best thought of as a cyclical process.
An iterative life cycle model does not
attempt to start with a full specification of requirements. Instead,
development begins by specifying and implementing just part of the software,
which is then reviewed to identify further requirements. This process is then
repeated, producing a new version of the software at the end of each iteration
of the model. It is specifically designed to
start with the bare minimum requirements and only construct a portion of the
program iteratively.
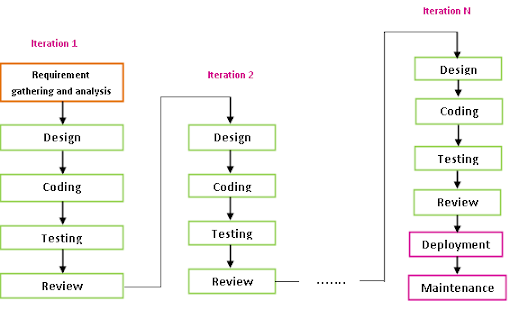
In this model, we can start with some of the software specifications and develop the first version of the software. After the first version if there is a need to change the software, then a new version of the software is created with a new iteration. It will repeat until deployment of the software.
The
various phases of Iterative Model are as follows:
Requirement gathering & analysis: In this phase, requirements are gathered from customers and check by an analyst whether requirements will fulfill or not.
Design: In the design phase, team design the software by the different diagrams like Data Flow diagram, activity diagram, class diagram, state transition diagram, etc.
Coding: The actual construction of
the system begins at this point in the project. All planning, specification, and design docs up to this point
are coded and implemented into this initial iteration of the project.
Testing: After completing the coding phase, software
testing starts using different test methods to identify and locate any potential bugs or
issues that have have cropped up. There
are many test methods, but the most common are white box, black box, and grey
box test methods.
Review: The review phase
is where the software is estimated and checked as per the current requirement.
Then, further requirements are reviewed discussed and reviewed to propose for
an update in the next iteration.
Deployment: After
completing all the phases, software is deployed to its work environment.
Maintenance: In the
maintenance phase, after deployment of the software in the working environment
there may be some bugs, some errors or new updates are required. Maintenance
involves debugging and new addition options.





0 Comments
if you have any doubts plz let me know...